|
|
|
Hansen's Northwest Native Plant Database |
|
|
|
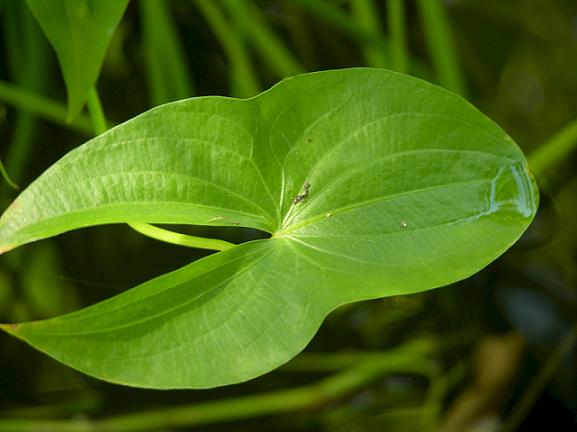
Sagittaria latifolia (Wapato, Arrowhead)
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Note: Throughout the years I've written short articles for our website's home pages (home pages are the front page of a website) about these plants. They are now included at the bottom of this page, and are illustrated by botanical drawings and paintings, some of which are from books published from 1500 - 1900. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The starchy edible tubers of the Wapato were a noted food source for Native Americans and Lewis and Clark and are currently enjoyed by ducks and other waterfowl. This plant is commonly found in wet swampy areas across the continental United States but is less abundant today in the Pacific northwest due to habitat destruction. The leaves grow above ground and are strongly arrow shaped. In mid summer, flower stems appear bearing white flowers with yellow centers. Grow them in USDA zones 3-10 along stream banks and lake or pond edges. This is an important plant in the restoration of riparian zones in sun or part shade areas. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Root - raw or cooked. Excellent when roasted, the texture is somewhat like potatoes with a taste like sweet chestnuts. The tubers can be eaten raw but they are rather bitter (especially the skin). It is best to remove this skin after the tubers have been cooked. The tubers can also be dried and ground into a powder, this powder can be used as a gruel or mixed with cereal flours and used to make bread. The N. American Indians would slice the boiled roots into thin sections and then string them on ropes to dry in much the same way as apples. The egg-shaped tubers are 4 - 5cm long and are borne on the ends of slender roots, often 30cm deep in the soil and some distance from the parent plant. The tubers are best harvested in the late summer as the leaves die down. They cannot be harvested by pulling out the plant since the tops break off easily, leaving the tubers in the ground. A poultice of the leaves has been used to stop milk production. A tea made from the roots is used as a digestive. A poultice of the roots is used in the treatment of wounds and sores. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Photos We Share!
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|